The Real Risks of Misconfigured S3 Buckets – and How to Lock It Down
In today’s cloud-first business landscape, Amazon S3 has become the default storage layer for everything from internal documents and backups to customer PII, API Secrets, and application logs. Yet despite S3’s scalable and powerful architecture, one silent misconfiguration is all it takes to cripple your entire business operations.
Thousands of companies have already been victims of this and paid the price. Data breaches, public backlash, massive compliance fines, and irreparable brand damage. Not because there was a complicated, advanced attack on the business infrastructure by cybercriminals, but because they left the front door wide open.
A misconfigured S3 bucket isn’t just a minor oversight, but a direct footpath for attackers to access sensitive data, hijack operations, and deploy malware into the business ecosystem. And the most overlooked part? Most organizations don’t realize their vulnerability until it’s too late.
1. What IS an S3 Bucket And Why It Matters:
Amazon Simple Storage Service S3 is a scalable object storage service used by developers, enterprises, and SaaS providers around the world. Each unit of storage, known as a “bucket,” is used to store critical data files like
- Backups
- Images
- Logs and more
2. The Real Consequences Of Misconfigured S3 Buckets

Massive Data Breaches
High-profile incidents involving companies like Accenture, FedEx, Verizon, and Dow Jones have all stemmed from exposed S3 buckets.
They Faced:
- Personal data leaks of millions of users
- Exposure of internal documents and source code
- Immediate press backlash
- Lawsuits and regulatory scrutiny (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI – DSS)
Credential Theft And Lateral Attacks
Misconfigured buckets often contain access tokens, API Keys, or IAM Credentials. Once exposed, attackers can navigate within your AWS environment, escalate privileges, and wreak damage beyond just the bucket.
Ransomware Via Public Write Permissions
An often overlooked risk: If public users can write to your S3 bucket, they can encrypt your files and demand ransom or overwrite them with malware.
- SEO Poisoning And Phishing Hosting
The most common use of an attack preferred by hackers after exploiting S3 buckets is to use the exposed S3 Buckets to host malicious content.
- Fake login pages to extract user information
- Malwayre Payloads
- Spam pages to manipulate search engine rankings and spread phishing campaigns.
- Hefty Fines
Governments and regulators treat data exposure seriously. Misconfigured S3 buckets can lead to:
- GDPR Penalties (up to £ 20 million or 4% annual revenue)
- HIPAA violations in healthcare
- SOX AND FINRA Violations in Finance
3. The Root Causes Of S3 Bucket Misconfiguration:
- Access Control Policies
Buckets with public-read or public-write permissions
Use * In IAM policies, exposing all resources
- Lack Of Encryption
- Absence of server-side encryption SSE
- Not enforcing encryption in transit using HTTPS
- No Monitoring Or Logging
- Disabled access logging or CloudTrail
- No real-time alerting for policy changes
- Manual Configuration Errors
- Human error in setting bucket policies or ACLs
- Lack of standardized security templates or CI/CD Integrations
- Default Settings Left Unchecked
- Buckets are set to private by default, but inheritance from templates, third-party tools copied configurations can introduce risk.
4. How To Lock Down Your S3 Buckets
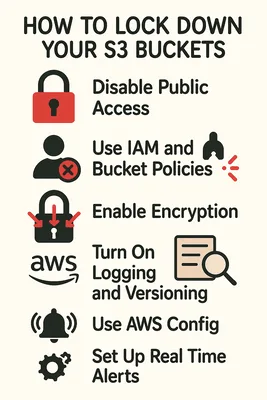
- Disable Public Access Account-Wide
Start by disabling public access at the AWS account level:
- Block public ACLs
- Block public bucket policies
- Ignore public ACLs
- Restrict public bucket policies
- Use IAM and Bucket Policies With Precision
Avoid using wildcards and overly broad permissions. Follow the principle of least privilege.
The key is to keep it simple.
- Grant only minimum required access
- Use resource-specific ARNs
- Regularly audit policies with AWS IAM Access Analyzer
- Enable Encryption (Both At Rest And In Transit)
- Use service-side encryption with AWS-managed keys (SSE-S3) or KMS (SSE-KMS)
- Enforce HTTPS access to your S3 bucket
- Turn On Logging And Versioning
- Enable S3 Access logs to another secure bucket
- Use AWS CloudTrail for API activity auditing
- Enable versioning to recover from accidental or malicious deletions
- Use AWS Config
- Set up AWS config rules to check for open buckets
- Use AWS Trusted Advisor to identify exposed buckets and inactive permissions
- Automate With Infrastructure As Code (IaC)
- Use tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation to deploy secure configurations
- Integrate with CI/CD pipelines for consistency
- Validate configurations with static analysis tools (Checkov, tfsec)
- Set Up Real-Time Alerts
- Use Amazon CloudWatch + SNS for real-time alerts on access pattern anomalies
- Monitor for new buckets or changes in policies
Final Thoughts:
In the cloud era, it’s your responsibility to secure your data against accidental exposure and malicious actors. Whether you’re a startup storing logs or an enterprise managing thousands of records, the need for airtight S3 security is universal. Don’t wait for a breach or regulatory fine to force action. Make S3 part of your core cloud strategy.
Partnering with experts like Webvoltz ensures your S3 buckets stay airtight, protecting your data, reputation, and your financial health
